The Conditions menu groups commands for setting restrictions on primers in your project. These commands allow you to specify template ranges, initial settings for amplification, primer lengths and thermodynamic characteristics, specific locations to search within the template, and metrics for evaluating primer/template mismatches for false priming.
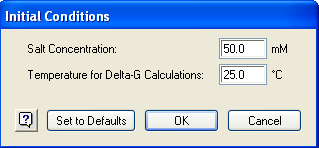
•Conditions > Initial Conditions allows you to modify the settings for salt (Na+) concentration and the temperature standard for computing free energy (∆G). The salt concentration chosen will affect the template melting temperature and free energy values calculated by PrimerSelect (see Thermodynamic models).
1) Select Conditions > Initial Conditions.

2) Input the Salt Concentration you commonly use.
3) Leave the default setting for Temperature for ∆G calculations unless you wish to explore values diverging from the thermodynamic models.
4) Click OK.
Note: Once you have set conditions, you may save them for use with future projects by selecting Conditions > Save Conditions.
•Conditions > Primer Characteristics allows you to set the parameters used when designing oligonucleotides for each template sequence. You can adjust parameters for Primer Length, 3’ Pentamer Stability, number of unique base pairs required at the 3’ end, acceptable hairpin and dimer duplexing, and more.
For instance, PrimerSelect may not initially show a dimer found in another software application. That is because dimerization negatively affects pairing with the template when it occurs at the 3' end of the primer where the polymerase binds, but has much less of an impact when it happens further away. For this reason, PrimerSelect enables you to control the distance from the 3' end of the primer where dimerization is considered. Ignoring duplexing at a set distance from the 3' end allows PrimerSelect to identify many otherwise useful primers. By default, PrimerSelect ignores hairpins and dimers that occur 8 bp from the 3' end.
1) Select Conditions > Primer Characteristics or press Ctrl/Cmd+K (Win/Mac).
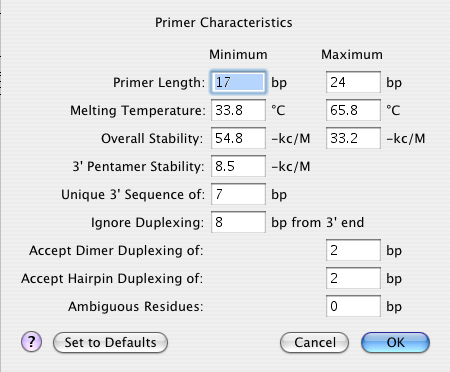
2) Input the Primer Length range for potential primers. The defaults are 17 and 24, respectively. Changing these values will change Tm and Overall Stability once you press the OK button in the final step.
3) Input the Melting Temperature range. The defaults for this option are based on the current template(s), so the option does not appear until you have entered a sequence. If you change the values, they should stay within the default range.
4) Input the Overall Stability range. The defaults for this option are based on the current template(s), so the option does not appear until you have entered a sequence. If you change the values, they should stay within the default range.
5) Input the 3’ Pentamer Stability threshold for the terminal five bases of a primer. The default value -8.5 kCal/mol is the average of all nearest neighbor pentamer interactions. Primers with pentamer ∆G more stable than -8.5 kCal/mol (more negative) have a tendency to false prime and are more likely to form hairpins and self-dimers. Modifying 3’ Pentamer Stability will change the median line plot in the Terminal Δ-G Plot View.
6) Input the Unique 3’ Sequence, the threshold that limits false priming. Using the default of 7, any primer without a unique seven base sequence at the 3’ end is rejected. Lowering the value makes primer selection more stringent.
7) Input a value for Ignore Duplexing N bp from 3’ end if you want to force PrimerSelect to ignore any hairpins or dimers a set distance from the 3’ end. The default is 8.
8) Input a value for Accept Dimer Duplexing to limit how many matching base pairs a self-dimer may contain. The default value is 2, but dimers with three matching bases seldom decrease primer performance unless close to the 3’ end.
9) Input a value for Accept Hairpin Duplexing to limit how many base pairs may be contained in a hairpin. The default is 2, but hairpins 3 bp long rarely affect performance unless close to the 3’ end.
10) 1Input a value for Ambiguous Residues to limit how many ambiguous residues can be used in a template area marked for hybridization. Using the default of 0, ambiguous residues in the template are marked and PrimerSelect will not allow the area to become a hybridization site.
11) Click OK.
Note: Once you have set conditions, you may save them for use with future projects by selecting Conditions > Save Conditions.
•Conditions > Primer Locations allows you to modify the limits on primer locations within the template. You can restrict primer locations by Product Length, Upper Primer Range and Product Length, Lower Primer Range and Product Length or Upper and Lower Primer Ranges.
1) Select Conditions > Primer Locations or press Ctrl/Cmd+L (Win/Mac).
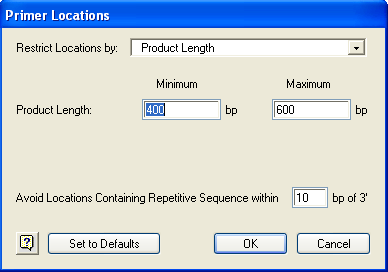
2) Use the list box to choose whether to Restrict Locations by Product Length, Upper Primer Range and Product Length, Lower Primer Range and Product Length or Upper and Lower Primer Ranges.
3) Fill in the Product Length and/or Primer Location range boxes, as prompted.
4) Input a value for Avoid Locations containing Repetitive Sequence within N bp of 3’. To utilize this function, you must define repeat sequences by selecting Conditions > Repetitive Sequences.
5) Click OK.
Note: Once you have set conditions, you may save them for use with future projects by selecting Conditions > Save Conditions.
•Conditions > Mispriming allows you to modify parameters which evaluate priming when primer and template are not identical. These values are used in determining false priming sites of a given primer and locating priming sites for Primer Catalog entries which do not identically match the template.
1) Select Conditions > Mispriming to open the dialog below:
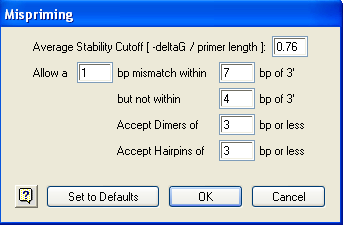
2) Input the Average Stability Cutoff. This value determines if a template location qualifies as a mispriming site based on its free energy / length.
3) Fill in the values for Allow an X bp mismatch within Y bp of 3’ but not within Z bp of 3’. The first field specifies the maximum size of the mismatch, the second specifies where to establish the range for this maximum value and the third specifies the minimal distance from the 3’ end which may not contain mismatches.
4) Input a value for Accept Dimers of N bp or less to limit how many matching bases a pair or self-dimer can contain. This parameter allows a distinct dimer threshold for misprimed oligos and does not affect dimers when the primer and template are identical. In that case, use Conditions > Primer Characteristics (Accept Dimer Duplexing of N bp).
5) Input a value for Accept Hairpins of N bp or less to limit how many matching bases a hairpin can contain. This parameter allows a distinct hairpin threshold for misprimed oligos and does not affect hairpins when the primer and template are identical. In that case, select Conditions > Primer Characteristics (Accept Hairpin of N bp).
6) Click OK to accept these settings and close the Mispriming dialog.
Note: Once you have set conditions, you may save them for use with future projects by selecting Conditions > Save Conditions.