
Note: This topic is not applicable to BAM-based projects.
Assembling parameters determine how constituent sequences are combined to form contigs. Access these parameters by selecting Project > Parameters and choosing Assembling from the list on the left.

First, choose an Assembly Method. For guidance on which assembly method to use, see Choosing Between the Classic or Pro Assemblers.
The following assembly parameters are available for editing:
•Match Size, the smallest number of matching consecutive bases required to extend comparisons between the new sequence and a contig or between two sequences. For the Pro assembler, the default is 25. For the Classic assembler, the default value is 12.
•Minimum Match Percentage, the minimum % of matches in an overlap required to join two sequences in the same contig. (Default is 80%)
o The Pro Assembler checks pairwise similarity in a rolling window of 50 bases to ensure that an extremely good match in one region does not compensate for a poor match in another. To qualify as having an above threshold similarity, the pairwise similarity must meet or exceed the value set in this parameter in each overlapping window.
o The Classic Assembler simply requires that the Minimum Match Percentage threshold be met over the entire alignment. Enlarging this threshold makes assembly more stringent but increases the likelihood of sequences that belong together not being joined. Decreasing it allows you to assemble sequences that do not match as well but increases the risk of making false joins between sequences that do not belong together.
Note: For more information on how Match Percentage is used for each assembly method, see Choosing Between the Classic or Pro Assemblers.
•Match Spacing (Pro assembler only), the preferred spacing of Understanding Mer Tags in a sequence. The default value of 150 dictates that the Pro Assembler will divide each sequence into sections 150 bases long and then choose one Understanding Mer Tags per section.
•Minimum Sequence Length, the threshold length of sequence that qualifies for addition to the assembly. If sequences are first trimmed for vector and/or quality, Minimum Sequence Length refers to the remaining length of the trimmed sequences. If you want to include in the assembly sequences smaller than the default value of 100 bases, simply enter a smaller number here. However, note that this value should be no less than the Match Size value specified above.
•Maximum Added Gaps per kb in Contig (Classic Assembler only), the maximum number of gaps that can be added to a contig while merging with a new sequence. If a new sequence requires that a longer gap be inserted in the contig, the new sequence is not allowed to merge. It will be checked against any other contigs before being considered for a new contig.
•Maximum Added Gaps per kb in Sequence (Classic Assembler only), the maximum number of gaps that can be added to a new sequence while merging with an existing contig. If a sequence requires a longer gap in order to be inserted in the contig, the new sequence is not allowed to merge. It will be checked against any other contigs before being considered for a new contig.
•Maximum Register Shift Difference (Classic Assembler only), the maximum separation, in bases, between nearby matches.
•Lastgroup Considered (Classic Assembler only), the maximum number of alignment groups SeqMan Pro investigates to see where a new sequence aligns with a contig. This must be set to one or higher. Alignment groups are groups of identical matches likely derived from the same region of a sequence.
•Gap Penalty, the penalty to be deducted from the pairwise score for each alignment for every gap introduced into either strand. Each gap incurs the same penalty regardless of its length. A high gap penalty suppresses gapping while a low value promotes gapping.
•Gap Length Penalty, the penalty assessed to gaps in the pairwise alignment step. This value deters long gaps by making them more costly than shorter gaps, proportional to their length. If it doesn't matter to you how long gaps are, this value can be set to zero.
The following options are only available if you select the Use Pro-Assembler button:
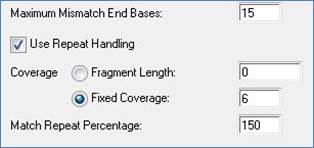
•Maximum Mismatch End Bases , the number of bases from an end where mismatches are not counted when computing the pairwise similarity between two reads. This parameter helps ameliorate the problems caused by untrimmed vector or bad base calls at the ends of reads. The default value is 15.
•Use Repeat Handling , a set of parameters that compute a threshold for determining the number of identical subsequences of bases, or mers, used to indicate a putative repeat. The Pro Assembler layout algorithm relies on mers that occur in overlapping regions of fragment reads. Mers that are common to two or more fragment reads are aligned to determine the overall layout of reads. The Use Repeat Handling parameters control which mers may be chosen as tags for overlapping reads. The threshold is computed as a percentage of the expected coverage in a project. Coverage can be determined using the length of the fragment being sequenced or specified as a fixed number. If Fragment Length is selected, the expected coverage is the Fragment Length value divided by the total length of all sequences in the project. If Fixed Coverage is selected, the value in Fragment Length is ignored and the Fixed Coverage value is used as the expected coverage. The threshold is computed by multiplying the Match Repeat Percentage (default is 150%) by the expected coverage. Any mer that occurs more frequently than the computed threshold is not considered for use in determining overlaps.