In the Alignment View, the capitalization and coloration of a residue conveys additional information about it.
Constituent sequences:
Coloring of constituent sequences is specified in the Editing & Color parameters (Project > Parameters > Editing & Color). Sequence residues that conflict with the consensus sequence are shown in the Mismatch color, which is red by default.
Consensus sequence:
Coloring of the consensus sequence is specified in the Variant Discovery parameters (Project > Parameters > Variant Discovery) and affects variant projects only.
Lowercase letters in the consensus sequence indicate one of three things:
•That the sequence read is in lowercase and there is single-sequence coverage.
•If using the Trace Evidence method, lowercase indicates that the sum of the weights for gaps is more than 25% of the total weight (the sum of the averaged qualities) for a column.
•If using the Majority method, lowercase indicates that the sum of the weights of the gaps exceeds 100-majority percentage times the total weight.
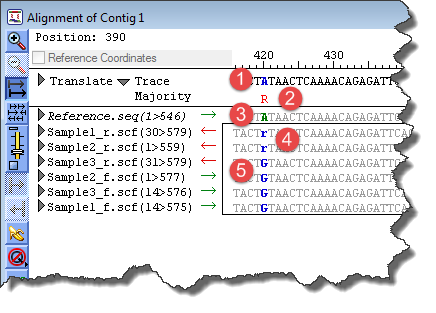
The following image and table are used to demonstrate the capitalization and coloring in a sample variant project Alignment View.

The italic type in the image above indicates that the Reference sequence is “marked.” See Specifying a Reference Sequence or The Project Summary Window for information about marking and unmarking Reference sequences.
When the Reference is marked, the consensus is identical to the Reference. This fact will influence the coloring of the residues. Where applicable, the table notes differences between Alignment Views with marked/unmarked References sequences.
|
Legend |
Letter |
Location |
Meaning |
Controlled via |
|
|
A uppercase blue/bold |
Trace |
The letter shows the trace evidence call for the consensus. The blue denotes that there is a putative variant at that position.
Since the Reference sequence is marked in this example, the entire consensus is the same as the reference. This is the reason the consensus is being called as “A.” If the Reference sequence were instead unmarked, the consensus would reflect the sample reads. |
|
|
|
R uppercase red/non-bold |
Majority |
The letter shows that the majority of samples are called as R (ambiguity code for A/G).
Since the Reference sequence is marked, the color red denotes a “mismatch,” meaning that the Majority call is different from the Trace call. The consensus in this case is a copy of the Reference and does not represent the actual Trace call. |
|
|
|
A uppercase green/bold |
Reference |
The letter is the nucleotide (“A”) at the given position in the Reference sequence. It is colored green to signify that that it matches the Trace call. |
|
|
|
r lowercase blue/bold |
constituent sequence |
The letter is the nucleotide ambiguity code for A/G. The lowercase type (“r”) denotes low confidence in the base call. The blue signifies that there is a putative variant at that position. |
|
|
|
G uppercase blue/bold |
constituent sequence |
The letter is the nucleotide (“G”) for these constituent sequences. The blue denotes that there is a putative variant at that position. |
Note: For coloring of trace data peaks, see Viewing Trace Data in the Alignment View.