In Part A of this tutorial, you will use raw data in PacBio CLR, PacBio HiFi or Nanopore format to create draft genome assemblies for seven SARS-CoV-2 samples using SeqMan NGen. You will then open one of the assemblies in SeqMan Ultra, generate a table of non-synonymous variants, and export one of the consensus sequences (i.e., “draft genomes”) in .fasta format. You can either stop at this point or proceed to Part B for further analysis of the experimental sample.
If you only work with draft genomes rather than raw long reads, you may skip this part of the tutorial and proceed directly to Part B.
- Download the tutorial data and extract it to any convenient location (i.e., your desktop).
- Launch SeqMan NGen and click New Assembly.
- In the Workflow screen, choose the Variant Analysis / Resequencing tab. Under PacBio / Nanopore, click ARTIC Amplicon.
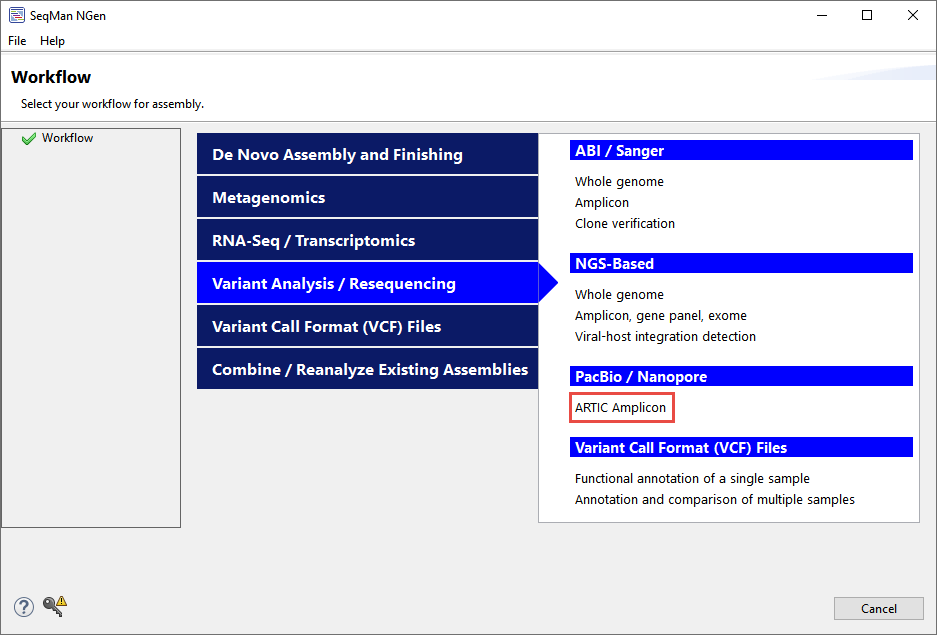
- In the Reference Sequence screen, click Add and add the file COVID reference genomes\NC_045512.2.gb, which is the original Wuhan strain of SARS-CoV-2. This reference sequence contains annotations for protein coding features.
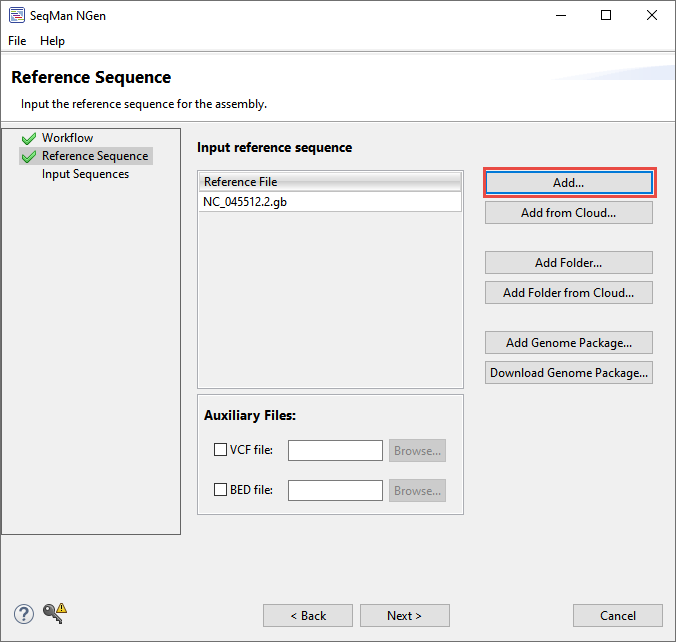
Click Next.
- In the Input Sequences screen, use the Read technology menu to specify PacBio HiFi and the Experiment setup menu to specify Multi-sample. Click Add and add all seven .fastq files from the PacBio reads folder. Each file contains several thousand reads and represents a unique sample.
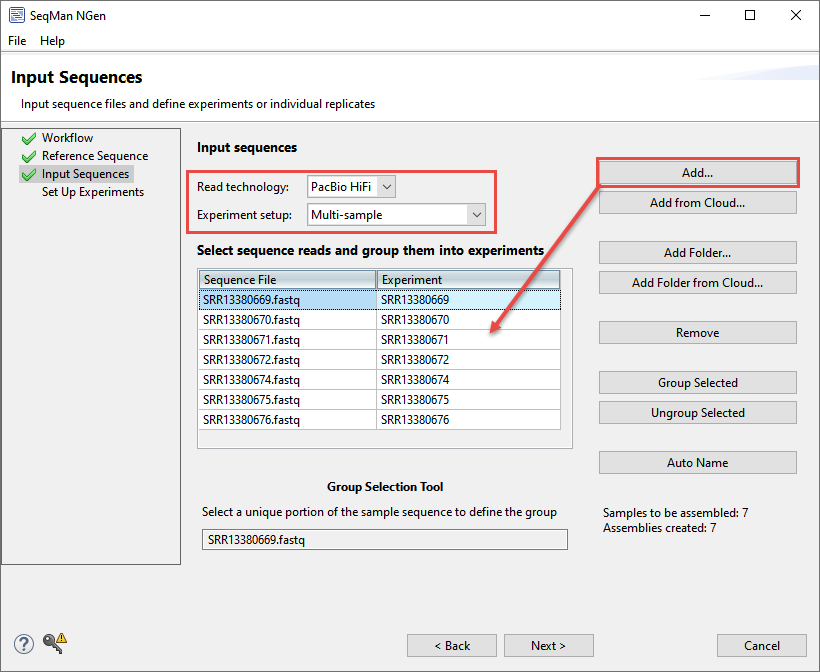
Click Next.
- In the Set Up Experiments screen, leave all boxes unchecked and click Next.
- In the Assembly Options screen, check the box next to Maximum total reads and input 1,000 in the corresponding box. This will limit the depth of the assembly so the data will assemble faster for purposes of this tutorial.
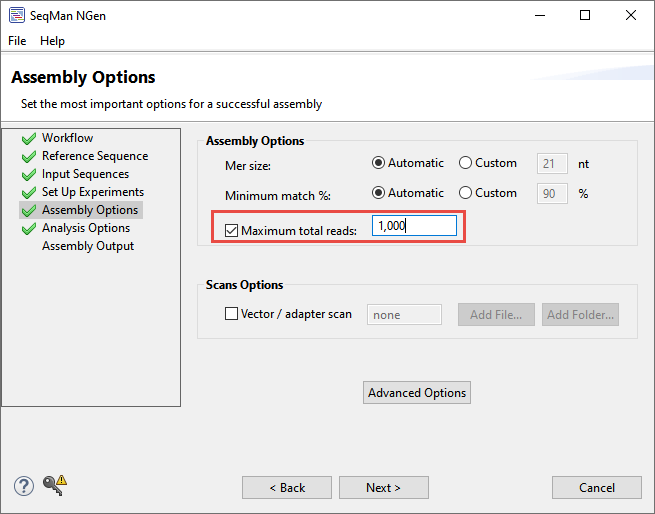
Click Next.
- In the Analysis Options screen, leave all default settings and click Next.
- In the Assembly Output screen, type CoV-2 samples next to Project name and use the Browse button to specify a folder for storing the results. Choose a location other than your desktop.
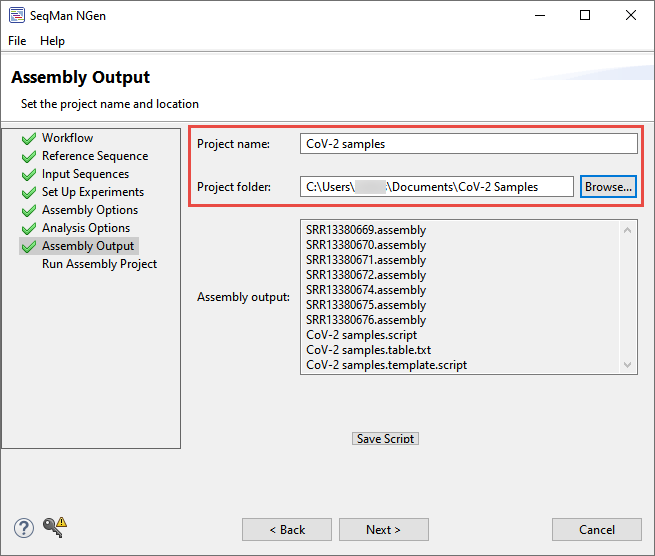
Click Next.
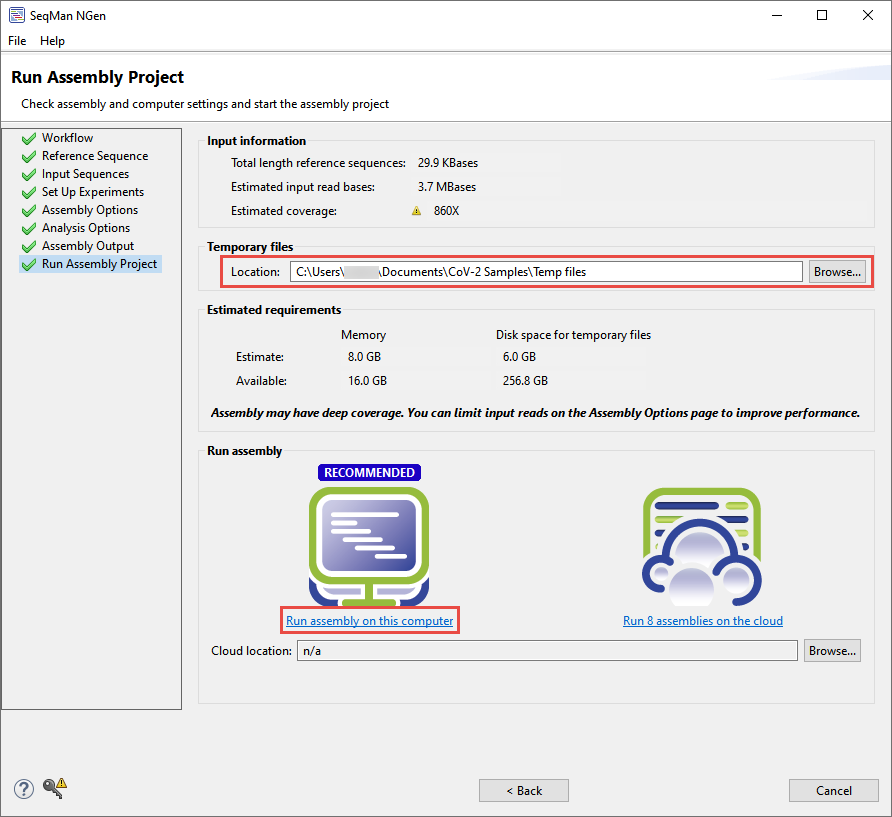
- In the Run Assembly Project screen, use the Browse button to specify a folder for storing temporary files. Choose a location other than your desktop.
- If you would like to run the assembly, select Run assembly on this computer. Assembly will take approximately 40-60 minutes.
- If you do not want to run the assembly, skip to step ___. The tutorial data includes a finished assembly that you can use for downstream analysis.
- If you would like to run the assembly, select Run assembly on this computer. Assembly will take approximately 40-60 minutes.
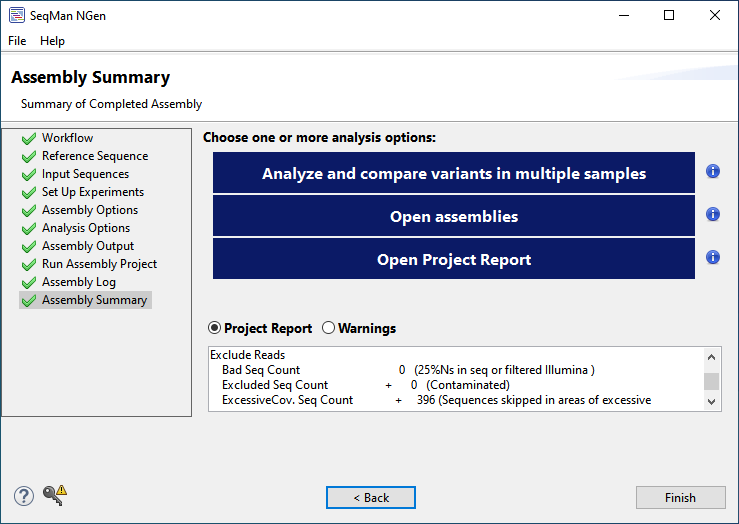
- Once assembly is complete, click Next at the bottom of the Assembly Log screen. In the Assembly Summary screen, note the options for downstream analysis, but do not press any buttons at this point.
- The Analyze and compare variants in multiple assembles button launches the results in ArrayStar, where you can easily compare multiple samples. For an example of this, see Part B of the whole genome reference-guided workflow tutorial.
- The Open assemblies button launches the results in SeqMan Ultra, where you can view the assembled draft genomes in graphical format with variants shown in a unique color scheme or examine and filter individual variants in the Variants table. For example, if you were studying SARS-CoV-2, you could use filtering to locate all non-synonymous variants in the spike protein. For an example of downstream analysis in SeqMan Ultra, see Part A of the long-read analysis tutorial.
- The Analyze and compare variants in multiple assembles button launches the results in ArrayStar, where you can easily compare multiple samples. For an example of this, see Part B of the whole genome reference-guided workflow tutorial.
You will next open the assembly result for a single strain of interest in SeqMan Ultra. You will then use SeqMan Ultra to export the consensus to analyze in MegAlign Pro in Part B.
- Open the experimental sample assembly.
- If you did run the assembly in SeqMan NGen, press the Open assembly button in SeqMan NGen’s Assembly Summary screen. In the popup, select SRR13380669.assembly and press OK. SeqMan Ultra launches with the assembly already loaded.
- If you did not run the assembly yourself in SeqMan NGen, launch SeqMan Ultra and use File > Open to open SRR13380669.assembly from tutorial data folder.
- Close SeqMan NGen by clicking Finish and responding Yes when prompted.
- Look at the Explorer panel in the top right of the SeqMan Ultra window. Note that a single contig was created and is currently selected. Open the Variants view by clicking the Show table of variants in selected contigs tool (
).
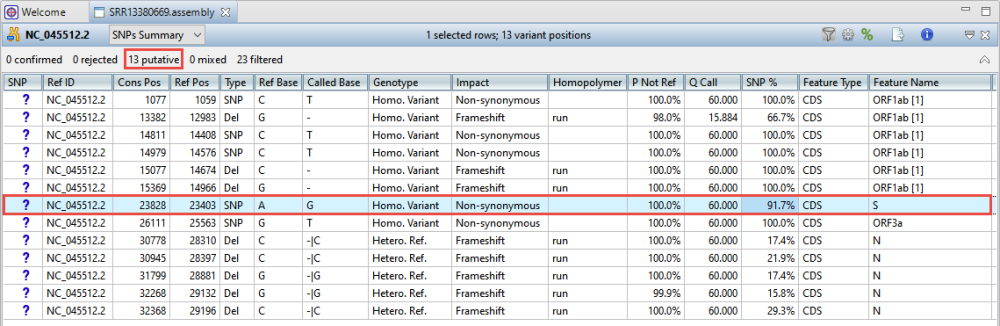
Look in the header to see that 19 putative and 3 filtered variants were found.
- To filter to show only non-synonymous variants, click the Filter all variant tables tool (
) in the top right of the Variants view.
- In the popup, remove the checkmarks next to Non-coding and Synonymous. Then press OK. The table now contains only the 13 non-synonymous variants. One of these is located in the SARS-CoV-2 spike “S” protein, shown as “S” in the Feature Name column.
- Export the contig using File > Export Data > Consensus > NC_045512.2. In the popup, keep the default settings and click OK. Name the file Spike variant.fasta and save it to any convenient location, including the desktop.
- Close SeqMan Ultra.
If desired, proceed to Part B: Using MegAlign Pro to determine the SARS-CoV-2 variant in an experimental sample.
Need more help with this?
Contact DNASTAR



 ).
). 
 ) in the top right of the Variants view.
) in the top right of the Variants view.