Brian Walsh, Ph.D., started his career as an instructor at the University of Wisconsin. Brian joined DNASTAR in 2016 and has spent 3 years in customer support, technical support, and software development and 4 years as the Scientific Lead for the MegAlign Pro application.
How to Create the Best Phylogenetic Tree for Your Data Using MegAlign Pro
How to Create the Best Phylogenetic Tree for Your Data Using MegAlign Pro

Introduction
In my early career as a phylogeneticist, I used whichever software was available in our lab. For the first few years, this was fine. But as my projects grew to include hundreds of samples, the software became increasingly cumbersome and unresponsive. In addition, I was needing to use 8+ often preposterously-complex applications to proceed from sequence data to a publication ready phylogenetic tree.
These experiences fueled my vision for MegAlign Pro as an easy-to-use application for any researcher interested in constructing phylogenetic trees and exploring evolutionary relationships between organisms. MegAlign Pro’s graphic-rich interface allows you to load in a variety of taxa (sequences), perform a multi-sequence alignment, then build a publication-quality phylogenetic tree; often in just a few minutes from start to finish. And all within a single application.
In Part A of this post, I’ll describe how to use MegAlign Pro to create a phylogenetic tree. Though MegAlign Pro is very easy to use, complex computational algorithms and parameters are involved behind the scenes in calculating the most accurate phylogenetic tree. These calculations determine things like which taxa are placed in a particular clade and the lengths and positions of tree branches.
In Part B, I’ll show you how to compare different versions of the tree using different algorithms and settings. In Part C, I’ll describe symptoms that indicate that the sequence data has some issues, and how to fix those issues.
Part A: Constructing phylogenetic trees in MegAlign Pro
There are only four steps needed to create and view a phylogenetic tree in MegAlign Pro.
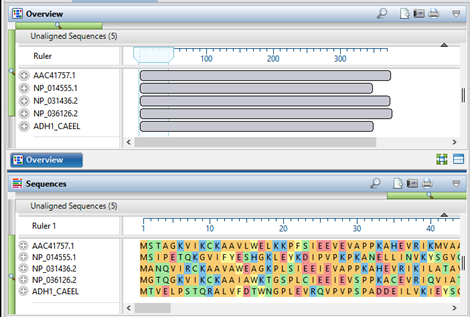
Step 1: Add sequences
Launch MegAlign Pro and use the Add sequences to project tool (green plus sign with “ACG”) to add two or more related taxa (sequences). The sequences must all be of the same type: DNA, RNA or protein.
Step 2: Choose a multiple alignment method and perform the alignment
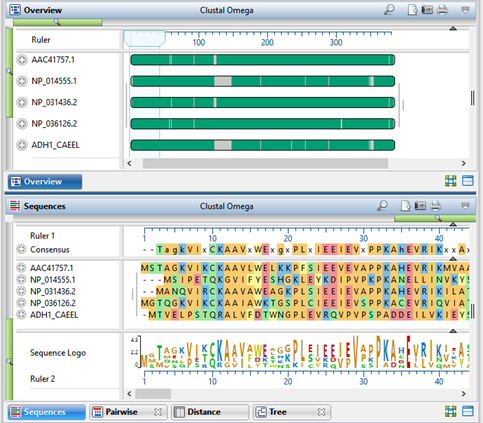
Specify the multiple alignment method and begin the alignment by pressing the Align tool (green button with white triangle) and choosing the desired method; or by using the Align > (Re)Align Using (Method Name) menu command. Method choices include Clustal Omega, ClustalW, MAFFT, MUSCLE; if nucleotide sequences are loaded, Mauve is also provided as an option.
To get the most accurate tree for your data set, please refer to our recent blog post, Two ways to find the best MegAlign Pro multiple sequence alignment method for your data.
Step 3: Build the tree
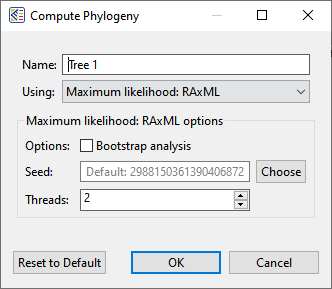
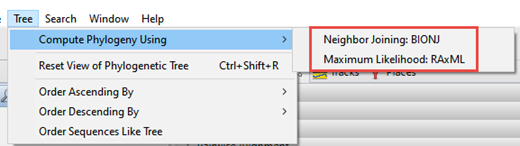
Once the alignment has finished, click on the Tree tab. Press the button for the desired tree calculation algorithm: Neighbor joining: BIONJ, Maximum likelihood: RAxML, or Maximum likelihood: RAxML-NG.

Which method should you choose when constructing phylogenetic trees?
– Neighbor joining: BIONJ is used for projects with fewer than 4 sequences, the minimum needed to use the RAxML methods.
– Maximum likelihood: RAxML can be used for data sets that are divergent, contain many taxa and/or very long sequences, or if you need to enter support (bootstrapping) values.
– Maximum likelihood: RAxML-NG is similar to its predecessor, RAxML, but is faster and has a larger capacity. This next-gen algorithm can be used for any data set with enough sequences, but is particularly useful for gene homology alignments, as it supports the creation of very large trees.
Step 4: View the tree and the distance table
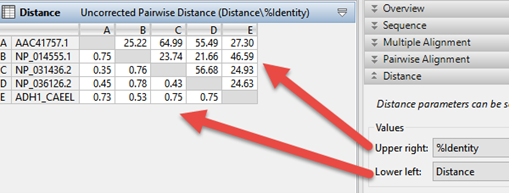
In the Tree view, notice the numbers on each branch: these are “distance” values. (If you don’t see numbers on the branches, use the Branch label menu in the Tree section of the Style panel to choose Distance.) “Distance” is the expected number of substitutions per site (base) and represents the degree of relatedness between two samples.
To view a customizable Distance table where you can examine the maximum likelihood phylogeny–among other values–click on the Distance tab. Use the Distance section of the Style panel to specify which two types of data (e.g., distance, percent identity, percent similar, percent gaps, sequence lengths, etc.) you’d like to see on the Upper right and Lower left of the Distance table.
Part B: Recalculating the tree using different algorithms or settings
Most of the time, I find that the “default” MegAlign Pro tree reflects the expected relationships between the taxa in my project. However, that doesn’t mean I don’t want to try out different settings to see how they affect that tree. Luckily for those of us with curious minds, MegAlign Pro makes it super easy to change settings and recalculate the tree as many times as we want.
Before I describe ways to recalculate a tree, I want to mention a very easy way to save and compare all the versions of your tree side-by-side: the Take snapshot tool, located in the upper right of the Tree view (see image).
Each time you change a parameter used to calculate the tree, MegAlign Pro will update the tree automatically and include a list of current settings in the tree header. To preserve a copy of each tree, along with the settings used to calculate it, use the Take snapshot tool.
And now for the customization options:
Option 1: Trim the “ragged ends” from your sequences
Do you have one sequence that sticks way out on the 3’ and/or 5’ end compared to other sequences? If so, you can trim off its ragged end(s) to get a more accurate alignment and tree.
Option 2: Choose a different multiple alignment method
To choose a different alignment method, use the Align tool (green button with white arrow) or the corresponding Align > Realign Using (Method Name) menu command. This will cause a new alignment to take place from scratch.
Option 3: Change the distance metric and/or gap treatment method
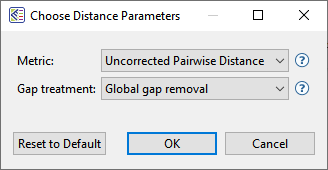
During the multiple alignment, distances are calculated using the Metric and Gap treatment specified in the Choose Distance Parameters dialog. This dialog can be accessed, and new options selected at any time, using Distance > Parameters.
– Choices for Metric are Uncorrected Pairwise Distance or Tamura-Nei (1993). In most cases, the two metrics yield essentially the same results. However, it is still worth changing to see how it affects your tree.
– Choices for Gap treatment are Global gap removal or Pairwise gap removal. Choosing Global gap removal can ruin the accuracy of the alignment and leave behind very little data with which to build an accurate tree. Unless you have a particular reason for choosing it, we strongly recommend choosing Pairwise gap removal.
Option 4: Change the tree building algorithm and/or parameters
As discussed in the first part of this post, there are three tree-building algorithms available in MegAlign Pro. To rebuild the tree using a different algorithm, or the same algorithm with different settings, choose Tree > Compute Phylogeny Using > (Method Name).
Part C: Spotting problems with the sequence data
Does one of your trees look… “strange”? In the vast majority of cases, an oddball tree is the result of issues with sequence data rather than with the algorithms or parameters used to calculate the tree.
This table shows–in no particular order—some of the symptoms, causes and solutions for issues related to sequence data.
Symptoms
Clades in the Tree view appear incorrect (e.g., a mammal appearing in a fish clade).
A branch in the Tree view is much longer (e.g., 20 times longer) than any other branches.
%Identity values in the Distance table are above 50%, indicating that the evolutionary relationship between the sequences is essentially random.
Likely causes
A sequence has been mislabeled or is unrelated to or highly divergent from the other sequences.
The alignment contains sequences in opposing orientations.
Possible solutions
Remove unrelated or highly divergent sequences and reassemble the remaining sequences.
Reverse-complement the sequences that need it and perform a new multi-sequence assembly.
© 2024 — DNASTAR Privacy Policy

